- SurveyJunkie: Make $5-$25 in your free time. Just take online surveys, participate in Focus Groups and trying new products. Join SurveyJunkie Now!
Are you prepared to learn the keys to strategic planning and financial success? Look nowhere else! Learn more about what AOP is in finance in this detailed article. Whether you’re a business owner, manager, or financial enthusiast, we have you covered.
What is AOP in finance? An annual Operating Plan (AOP) is a technique for forecasting and planning for a predetermined time frame. It includes key performance metrics, capital expenditure plans, profit objectives, and predictions of revenues and expenses.
We’re eager to be your dependable travel partner as the adventure begins here! Keep reading to get helpful suggestions, valuable insights, and professional advice on managing the complexities of AOP. Prepare to improve your knowledge of financial management and open the door to corporate success.
Table of Contents
What is AOP in Finance? Core Concept
There are various aspects to AOP. Let’s uncover each:
Explanation of AOP as a financial forecasting tool
What is AOP in finance? Organizations may plan and budget their operations for a certain period, usually one year, using the Annual Operating Plan (AOP), a financial forecasting tool. To help with decision-making and resource allocation, AOP focuses on measuring and estimating financial elements.
Components and elements typically included in an AOP
- Revenue projections: AOP provides an overview of anticipated revenue streams, considering sales predictions, industry trends, and consumer demand to evaluate the company’s financial standing and room for expansion.
- Expense forecasts: Forecasted expenditures are broken down among departments, such as operations, marketing, human resources, etc., by AOP, assisting in cost management and preserving profitability.
- Profit margins and targets: AOP establishes Profit margins and objectives using historical data and industry benchmarks, allowing performance to be evaluated and problem areas to be found.
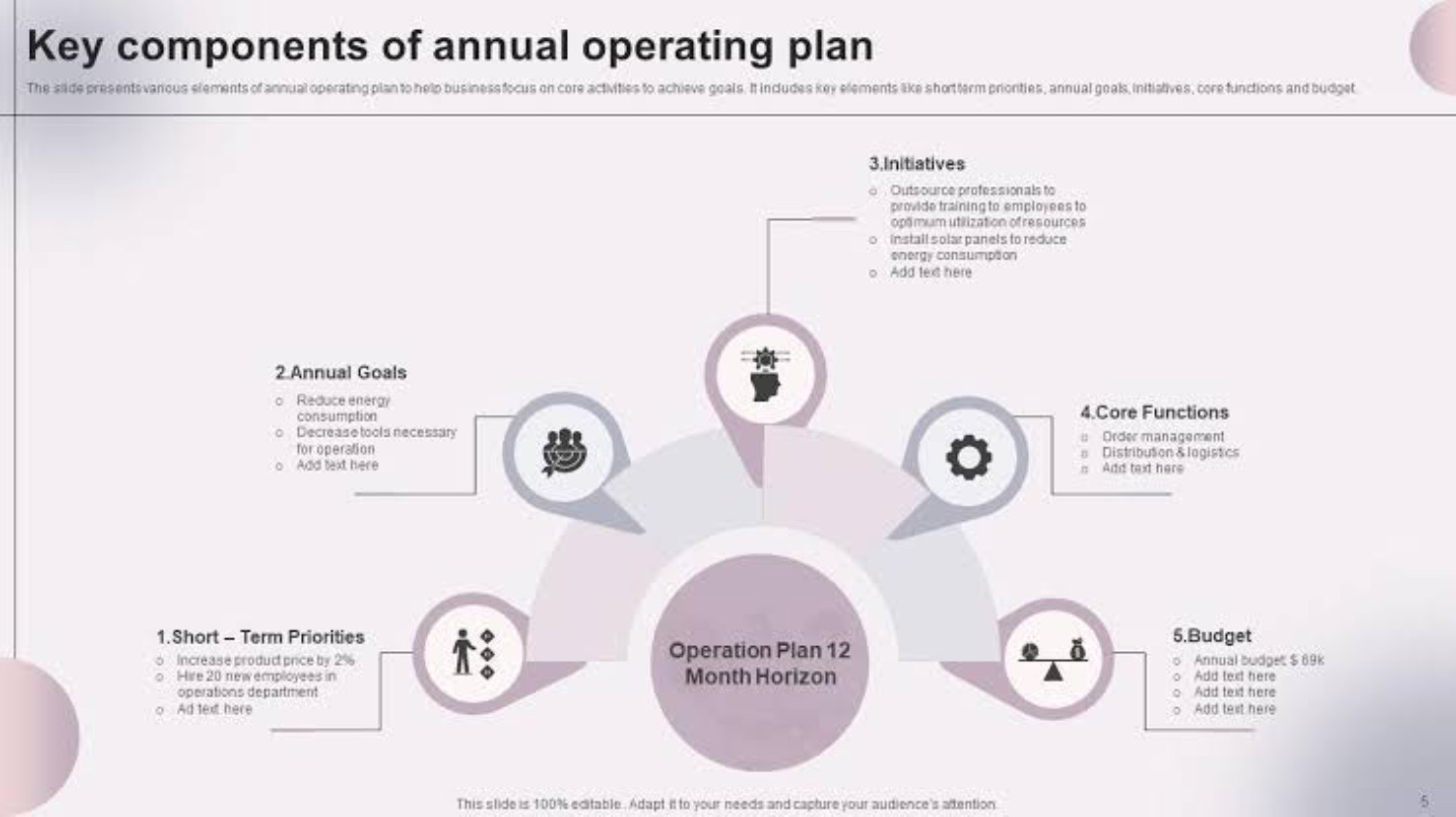
- Planning for capital expenditures: AOP allots money for long-term investments, coordinating capital expenditures with organizational objectives for effective resource management and strategic expansion.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs): KPIs used in AOP to gauge success and monitor development include revenue growth, profit margins, return on investment (ROI), expenses associated with client acquisition, and staff productivity.
See also: 10 Best Short-term Certification Courses in Finance in 2024
AOP Development Process
Steps involved in creating an AOP

- Gathering historical financial data: The AOP creation process starts with collecting and evaluating previous financial information, such as revenue, costs, and other pertinent indicators. This historical view offers a basis for comprehending the last performance and spotting trends that might affect estimates in the future.
- Analyzing market trends and competitive environments: When creating an AOP, organizations must consider external elements, including macroeconomic circumstances, market trends, industry outlooks, and competitive environments. Making accurate estimates and adjusting the strategy to the current business climate are made more accessible by analyzing these elements.
- Establishing financial goals and targets: AOP development is necessary to develop clear financial objectives that support the company’s strategic goals. These goals must be quantifiable, time-limited, and pertinent to the business plan. You’ll be more focused and capable of making wiser judgments each year if you have set clear financial goals.
- Establishing budgets and allocating resources across several departments or projects: AOP involves giving funds and resources to various departments or projects on their priorities and expected outcomes. This method facilitates cost control, promotes resource planning, and assures effective budget allocation.
- Reviewing and updating the AOP in light of comments and new information: The AOP should be a living document susceptible to adjustment as the business environment changes. Organizations may make the required modifications and ensure the strategy stays relevant and successful by regularly monitoring, soliciting stakeholder input, and analyzing insights from actual performance.
See also: How to Budget (Budgeting for Dummies in 2024)
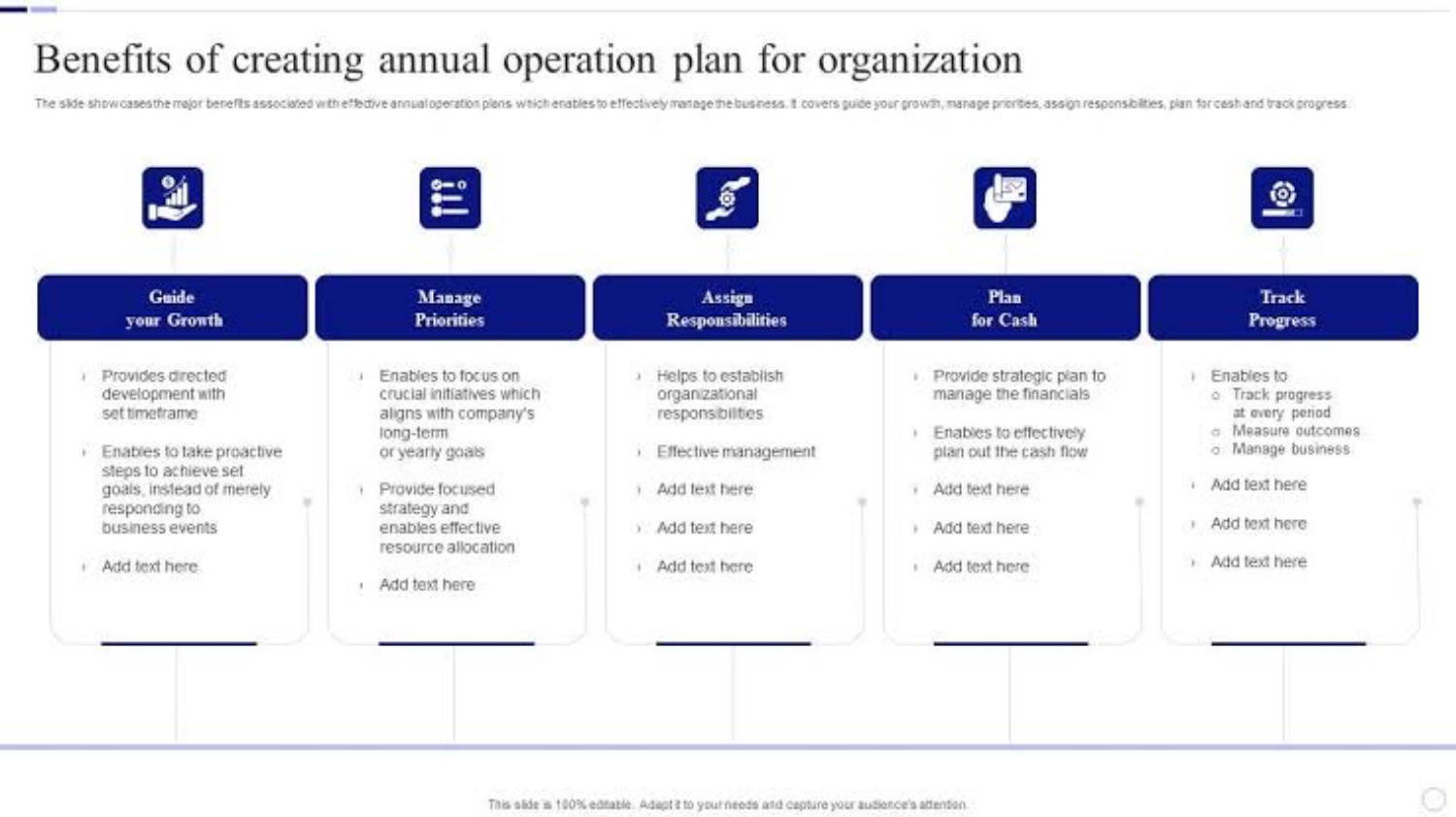
Importance and Benefits of AOP
Establishing financial goals and benchmarks for the organization
The AOP acts as a manual for setting precise financial objectives and standards for the business. It fosters a feeling of direction and purpose by offering a defined strategy that helps align the activities of multiple departments toward shared goals.
Facilitating strategic decision-making and resource allocation
AOP offers financial analysis and estimates to assist in strategic decision-making. It lets businesses decide which investments to prioritize, how best to use their resources, and what decisions best fit their long-term goals.
Enhancing financial discipline and accountability
An organization’s financial discipline is encouraged by AOP. AOP promotes accountability and helps pinpoint areas that need corrective action by comparing actual performance to the plan. It establishes benchmarks for profitability, cost control, and revenue development.
Assisting in performance evaluation and variance analysis
AOP serves as a yardstick for assessing performance all year long. Organizations can examine variations and pinpoint their causes by comparing actual outcomes to the predicted statistics. This analysis makes it easier to continuously improve and take corrective action to get the desired results.
Providing a basis for financial reporting and tracking progress
AOP provides a standardized framework for monitoring progress toward financial goals, which forms the foundation for financial reporting. Organizations can use it to produce accurate financial accounts and compare their performance to set goals.
See also: M1 Finance Vs. Robinhood – Which One To Use?
Challenges and Considerations
Limitations of AOP as a static plan in a dynamic business environment
AOP has inherent limitations as a fixed plan in a changing business context. Market circumstances, client tastes, and other outside factors might change quickly, necessitating plan revision and adaptation.
Dealing with uncertainties and unforeseen events
AOP could experience unanticipated circumstances and uncertainties that affect financial expectations. The accuracy and dependability of the plan may be threatened by changes in the economy, legislation, the weather, or the business environment. Organizations should be prepared to modify their strategy in reaction to such circumstances.
Balancing flexibility and accuracy in forecasting
AOP necessitates a balance between predicting accuracy and flexibility. Although businesses must be flexible and agile, reliable projections are essential for efficient decision-making. To keep the plan current and trustworthy, striking the ideal mix between accuracy and flexibility is crucial.
Involvement of stakeholders and coordination across departments
Stakeholders from different departments must actively collaborate to develop and implement an AOP. Accurate data, insightful observations, and buy-in from all pertinent stakeholders can only be attained via collaboration and communication.

See also: Personal Capital vs. YNAB: Which One Is Better?
AOP vs. Strategic Planning
Differentiating AOP from strategic planning
AOP acts as a comprehensive plan for a set period, often one year, and concentrates on the financial elements of an organization’s activities. On the other hand, strategic planning has a broader reach and goes beyond financial concerns to include long-term objectives, market positioning, competitive analysis, and resource allocation.
Understanding the relationship and alignment between the two
Strategic planning and AOP are related. AOP provides the financial foundation for implementing strategic plans, and AOP puts these goals into monetary terms and directs their implementation, whereas strategic planning determines the overarching direction and objectives.

See also: How does Snap Finance Work?
FAQs
Some frequently asked questions on ‘What is AOP in finance’ are as follows:
What is AOP in finance?
In finance, AOP stands for the annual operating plan. It is a tool for financial forecasting and planning that businesses use to allocate resources, define financial targets, and direct decision-making over a predetermined time frame, often one year.
What function does an AOP serve in finance?
The AOP is a manual for managing finances, allocating resources, and assessing performance. An AOP's primary function is to give a company a detailed financial roadmap. It aids in establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), profit margins, and estimates of revenues, expenses, and capital expenditures.
What elements do AOPs typically contain?
Key performance indicators (KPIs), profit margins and objectives, capital expenditure planning, and revenue and cost predictions are standard components of an AOP. These elements offer a comprehensive picture of an organization's financial performance and serve as a basis for decision-making.
How does an AOP become created?
AOP development is a multi-step process. The collection of preliminary financial information, analysis of market trends and business circumstances, formulation of financial goals and targets, budgeting and resource allocation for various departments and projects, and routine review and revision of the plan in light of feedback and new information are some.
What distinguishes an AOP from strategic planning?
AOP provides the financial foundation to enable the execution of strategic initiatives. An AOP covers a specified period, often one year, and primarily focuses on the financial elements of an organization's operations. On the other hand, strategic planning includes more extensive factors than only financial ones, such as long-term objectives, market positioning, competition analysis, and resource allocation.
How frequently ought an AOP should be examined?
An AOP should be evaluated often during the year to compare actual results to estimates and consider any business environment alterations. It is advised to perform formal evaluations at least once every three months and to make changes as necessary to maintain the plan's current functionality.
Conclusion:
An effective financial instrument that helps establish goals and improve financial management is the annual operating plan (AOP), which comprises revenues, costs, profit margins, capital spending, and KPIs predictions. This article addressed the issue of “What is AOP in finance” and preached several topics.
